Definition 7.1.1. Holonomic Constraints.
Constraints which lead to equations of the type
\begin{equation}
f(\bq, t ) = 0\tag{7.1.1}
\end{equation}
are said to be holonomic constraints.
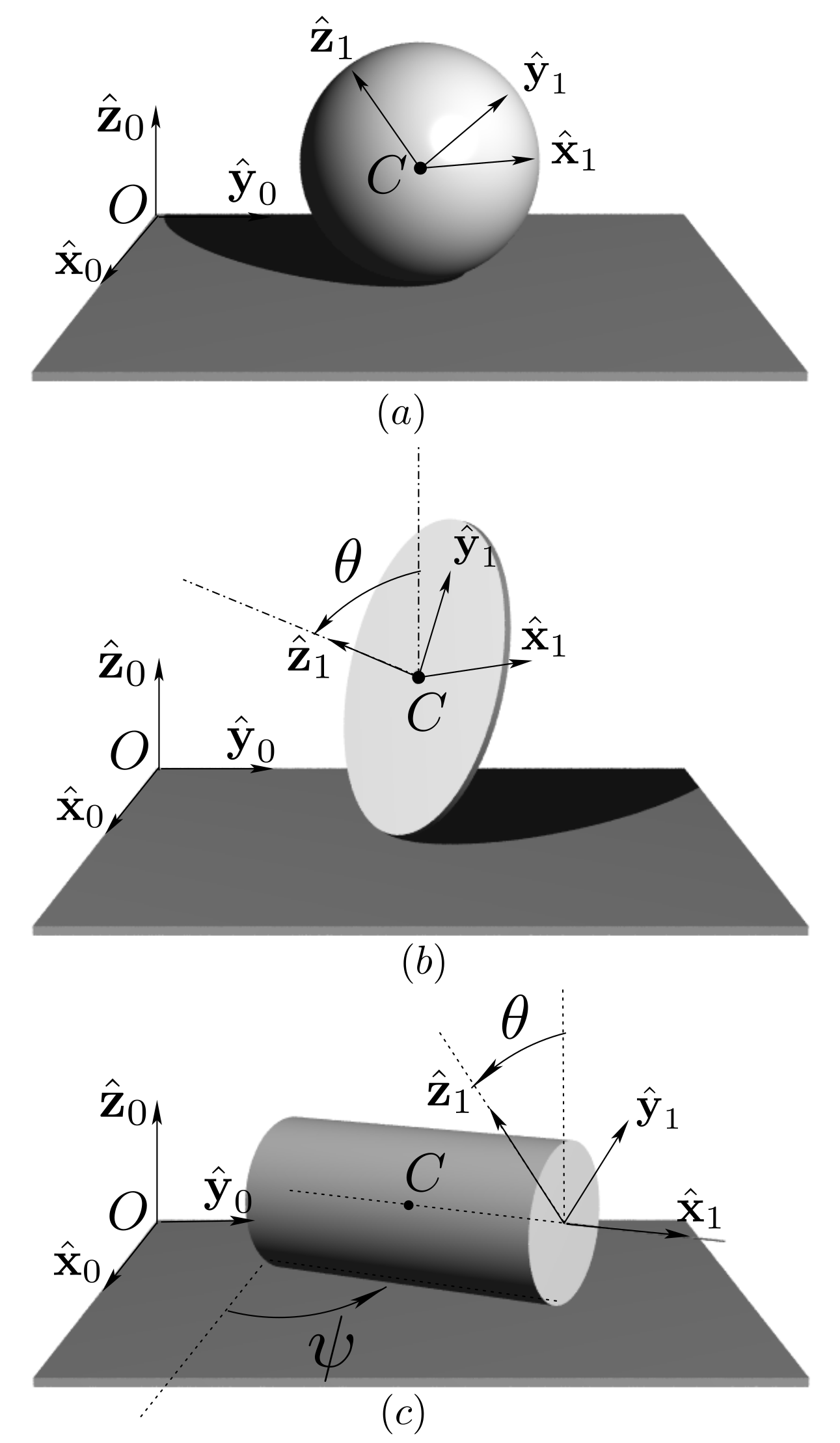
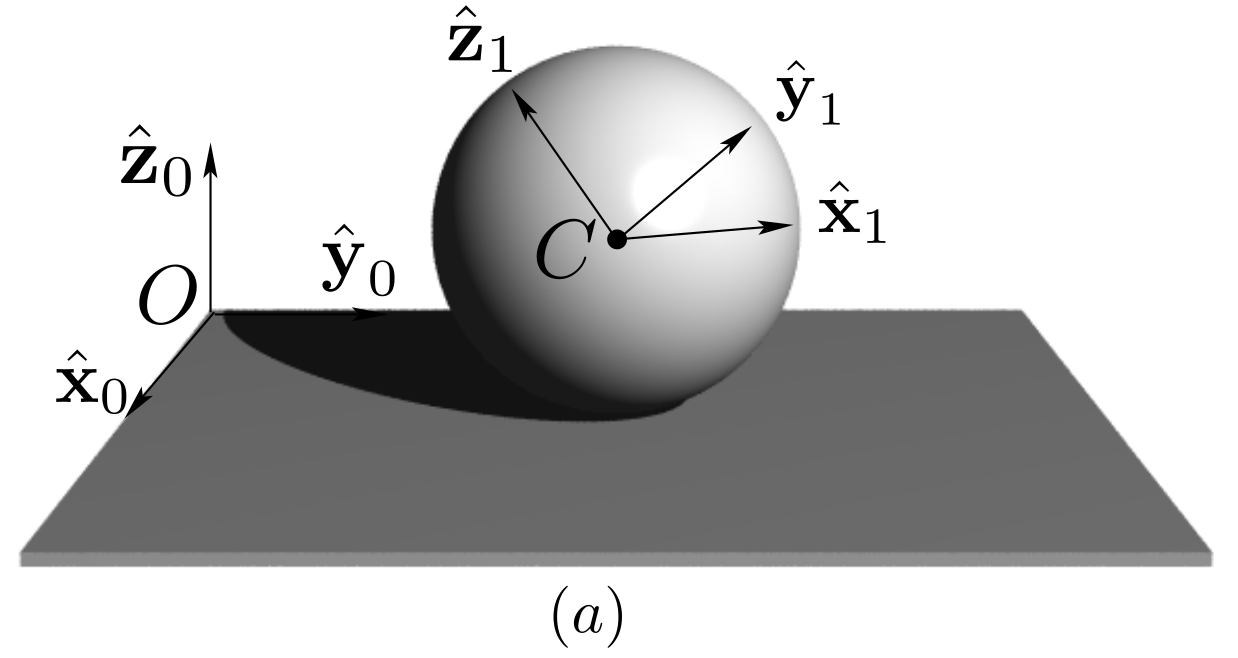
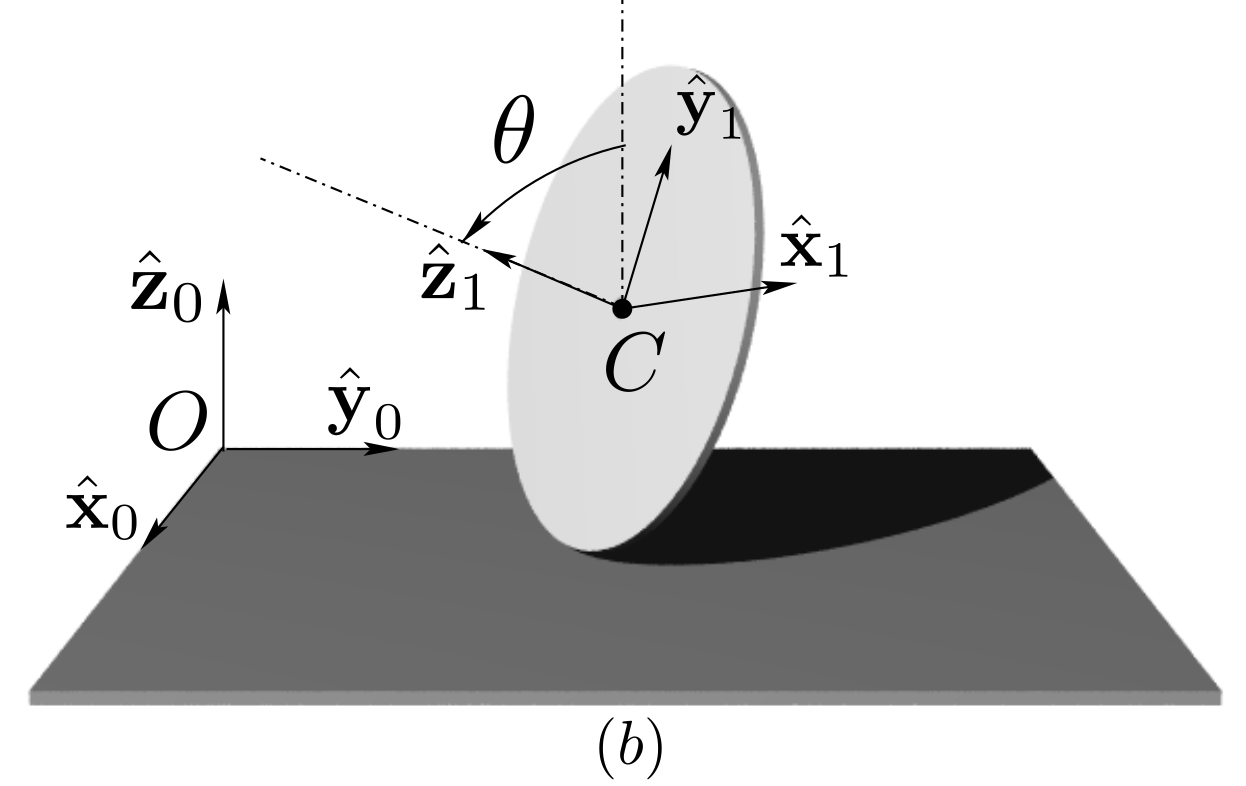
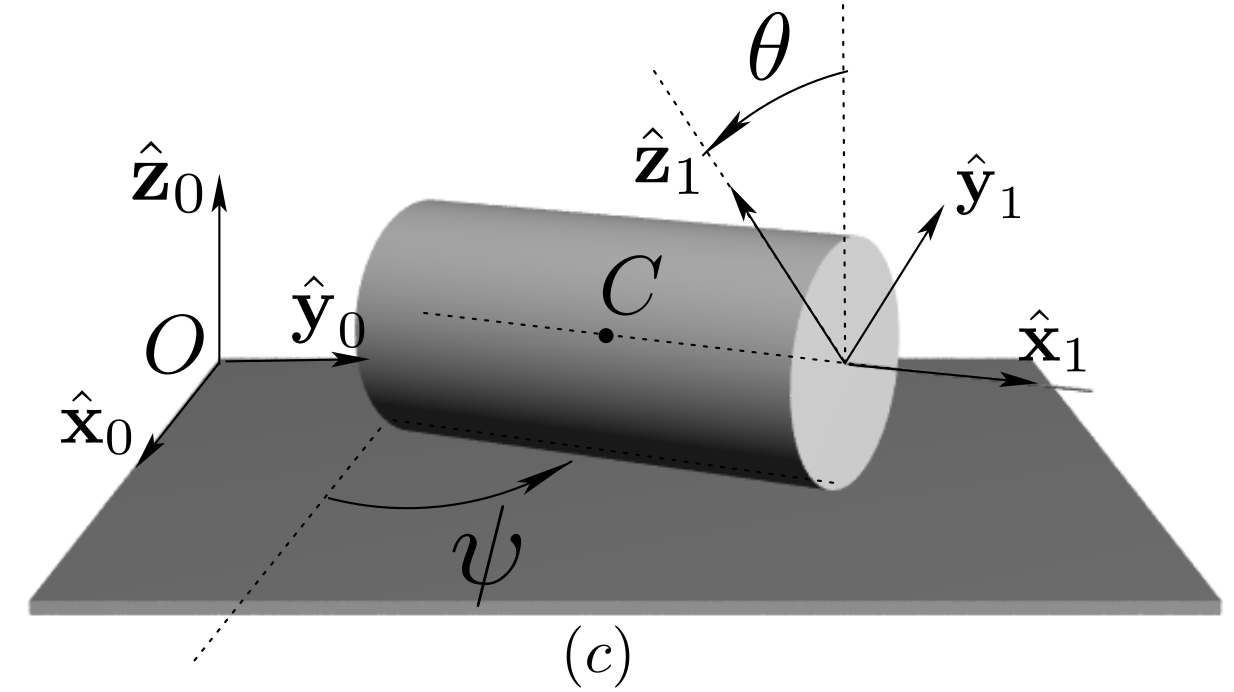
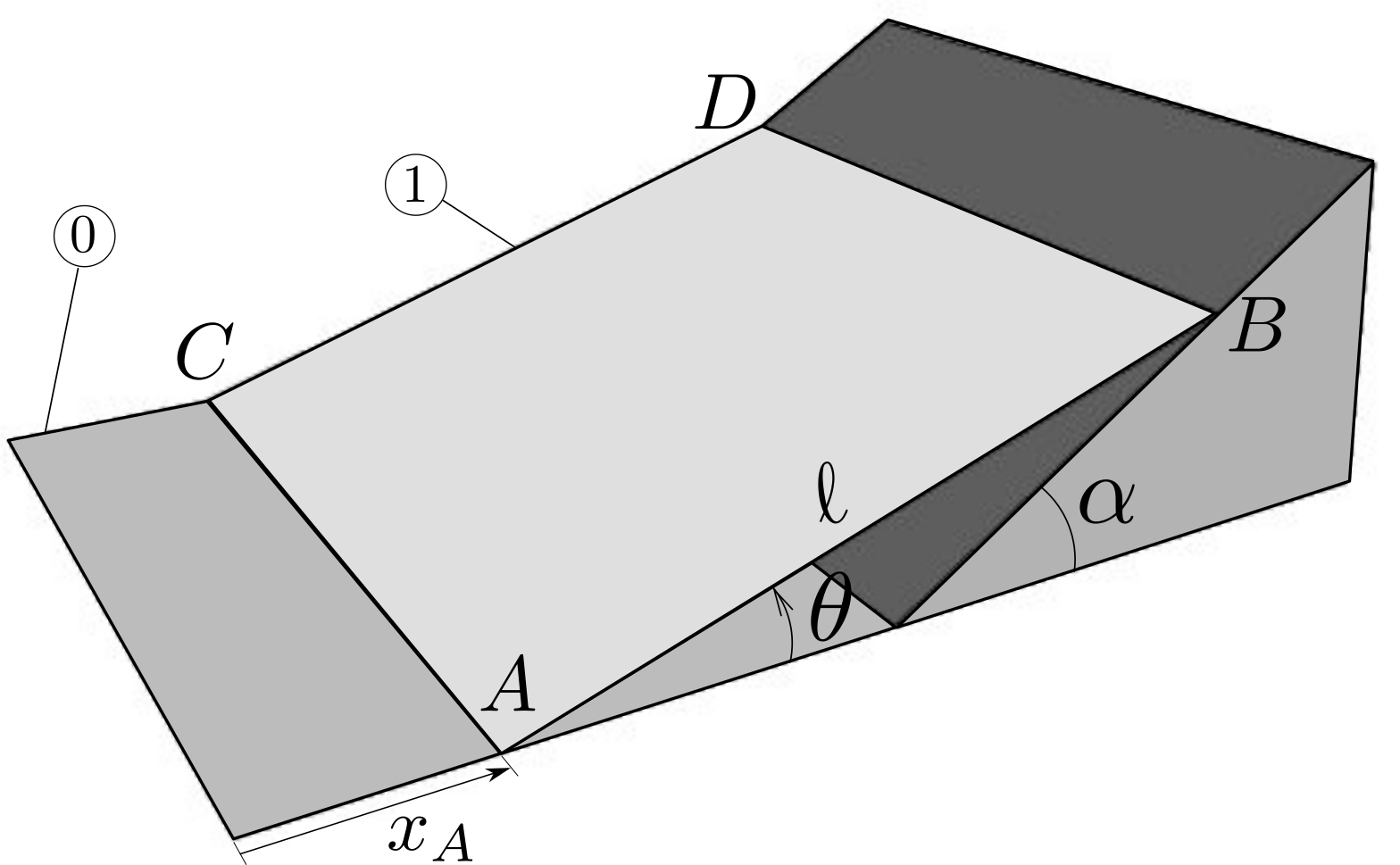
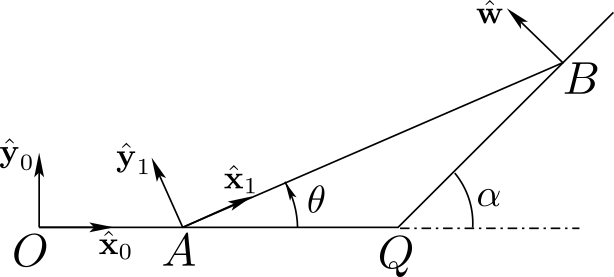
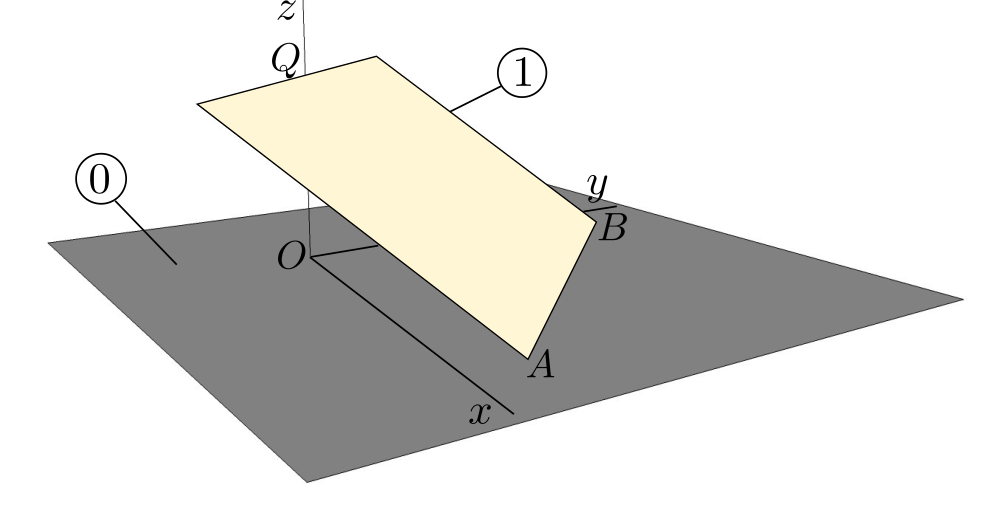
0 \((O, \bx_0, \by_0, \bz_0)\) denotes the pump housing. A piston thrust plate is attached to 0 and is inclined with constant angle \(\alpha\text{.}\) The value of angle \(\alpha\) can be adjusted to vary the pump volumetric volume.1 is the rotationally-driven pump barrel: it is rotating relative to 2 is a piston connected to 1 by sliding along axis \((B, \bx_0)\text{.}\) Only one piston is shown in the diagram. Piston 2 is in contact at all time with the inclined thrust plate at a point \(J\text{.}\) A spring (not shown) guarantees that contact is always realized.