Heat Transfer MEEG 342 - Assignments
Due Date Feb. 18th, 2004 (WEDNESDAY at 10:10 am in room Spencer 114).
Heat Transfer phenomena plays an important role in many industrial and environmental problems. We will devote much time to acquire an understanding of heat transfer effects and to develop skills needed to predict heat transfer rates. In order to get familiar with the subject, please follow the following procedure:
1. Think of one "Real World Application" of Heat Transfer (in cooking, manufacturing, climate, energy production and conversion, water heating systems, propulsion, internal combustion engines, cryogenic storage equipment, electronic cooling, air conditioning and refrigeration systems, etc.).
2. State the physical problem.
3. Sketch the problem with a figure.
4. Explain the physics of the process as you understand it.
5. Identify the important variables, what is known and you can control (independent variables) and what is unknown (dependent variables).
6. Identify the relevant physical laws that apply here.
Check out the Webpage http://www.howstuffworks.com/refrig.htm
to see the simple explanation of how a refrigerators work. Your goal in
this assignment will be to pick a simple or a complicated example and explain
( in a language that a high school student can understand) how and
why your selected "Real World Application" of Heat Transfer works.
Due Date Feb. 25th, 2004.(WEDNESDAY at 10:10 am in room Spencer 114)
Problem nos (using 4th Edition)
1.8, 1.10,1.18,1.21,1.28 and 1.30
Answers:
1.8
35.9 W
1.10
Al=110.40 C , Cu=110.25 C
1.18
Air=0.35 W. Dielectric=5.25 W.
1.21
qelec= 15 mW.
1.28
(a) q=18, 405 W (b) E=11 5.80 10 J ´(c)$6450
1.30
3.5%.
Design Problem:
Design an experiment to measure
thermal conductivity of most materials. State the apparatus needed and
describe the procedure. Also mention
how you would make sure that the heat losses in the experiment are
minimized.
Due Date March 3rd, 2004 (WEDNESDAY at 10:10 am in Spencer 114)
Problem no 2.12, 2.17(a), 3.4(a) and (b),3.9 and 3.13
Design Problem:
To brighten up the 5 degree Celsius winter days, your family has decided to add a sunroom to the house and you have been designated “lead engineer.” You have decided that the room will have four identical walls, each with an area of 20 m2, and twenty percent of each wall will be windows. Your family maintains that an indoor temperature of 20 degrees Celsius is the most comfortable. To keep bills down, the maximum heat transferred to one wall has been set to 900 W. Given this information, choose an insulation material with the proper thermal conductivity and thickness to maintain a temperature of 20 degrees Celsius inside on cloudy days with windy conditions, with the specifications of the room below.
Answers
2.12 qx at x=0 is 18.75 and at x=L is 16.25
2.17(a) k= 15.0 W/mK at 400K
3.4(b) qo" =2833 W/m2
3.9 kB=1.53 W/mK
3.13 (b)q=4.21 KW (c) 0.5 % in q
Due Date March 10th, 2004.
Problem no 3.43, 3.57, 3.72, 3.79, 3.109
Design Problem:
Design of fins
An electric heater is made by sandwiching
a heating element between two thin plates 40-cm long and 40-cm
high. When operating with air
at 20C the heater is to transfer 3000 W with a maximum plate temperature
of
120C. Propose a suitable
system of cylindrical fins. Minimum diameter of the fins should be 3mm
with a
minimum pitch of 4d. Weight and
volume are to be kept low. A fan forces air through the heater with a velocity
of 5 m/s so that the convective
heat transfer coefficient to the air is 80 W/m2C.
Answers
3.43 I=889
Amps
3.57 k= 0.062 W/mK
3.72 Tmax= 212C
3.109 Tb=300
Due Date March 17th, 2004
Problem no 5.5, 5.10, 5.37,5.55, 5.72, 5.88
Answers
5.5
t=1122s
5.10 t=968s T=456C
5.37 t= 491s
5.55 h =197.7 W/m2K and t=579s
5.72 t=1793s
5.88 Tcenter =434K and T corners= 320K
Due Date April 7,2004
6.29,6.35,6.39,7.9(a),7.20(a) and (c),7.28
6.29:(a) 34.3 W/m2K (b) h=59 W/m2K
6.35: Ts=42.5
6.39 hi=38.3 W/m2K
7.9a: q1 =51.1 W, q5=12.2W, q10=8.3W, q(0-25)=255.3
W
7.20a Ts,0 =33.8C, q=797
7.20c Ts,o= -9.9C, q=90,636 W
7.28 x=1 m, dT/dt= -0.987 K/s, at x=100m,
dT=dt = -1.47 K/s, minimum cooling rate where the flow transitions from
Laminar to turbulent
Due Date April 14,2004
7.47(a)(b)(c), 7.62a, 7.70, 8.16a,8.26,8.30a
Answers
7.47 (a) h=235
W/m2K
7.47(b) 0.868 W (c) 1.019 W
7.62a Hint: Use 7.57 to find h and check Bi number. If Bi number is greater than 0.1 use one term series approximation in section 5.6.2 to find the time to =15.2 s
7.70Using
find h and T. For water h=3559 W/m2K and Ts=18.7C.
For Air h=20.1 and Ts=672C
8.16a Tmo =113.5C, Ts,i=60C, Ts,o= 153.5C
8.26 q=-1281W and L=15.4 m
8.30a Tm,o=61.3C, q=1519W
Due Date April 23rd, 2004 (Friday)
8.36, 8.44, 8.52,8.62, 9.13, 9.38
Design Problem
An array of 4 evenly-spaced heat generating
electrical components is mounted on a base plate through which 11 holes
are drilled. One Kilowatt of heat needs to be extracted from
each component in order to maintain the temperature of these components
at 40 deg C. This is accomplished by moving cold water through the
cylindrical channels. The base plate is 30 cm long,15 cm wide and
2 cm thick. The water is available from the local supply at 25C. Select
the diameter of the holes and the mass flow rate such that the pressure
requirements to pump the water through these holes are minimum.
Answers
8.36(a) L=8.87 m, (b) Twall max =52.4C
8.44 (a) Tm,o =50C (b) Tm,o= 51.7C
8.52 q'= 312 W/m
8.62 (a) hi =409 W/m2K (b) ho= 97.5 W/m2K
(c) Overall heat transfer coefficient U=78.8 W/m2K (d) Tm,o =15C
9.13 heat loss due to convection=11.7 W, heat
loss due to radiation assuming emmissivity of 1 = 21.4W
9.38 (a)k=0.56 W/mK (b)h=7.87 W/m2K (c) e=0.815
Assignment #9
No Due Date. Solutions will be mailed to you
11.10, 11.20,11.26,11.45 and 11.69
Due Date: May 12th, 2004
12.10a, 12.14a,12.16,12.20,13.2 , 13.9a,13.19
Answers
12.10 a
12.14 a) radiation +133 W, convection 75.7 W, Pelec =232.7W
12.16 498K
12.20
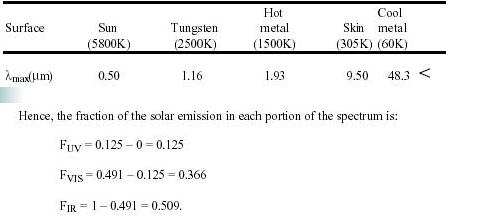
13.2
13.9
13.19 F13 =0.64 and q13 = 1700W
Assignment #11 (Last Assignment)
Due Date: May 19th, 2004
13.34(a)(b)(c), 13.58,13.62,13.71(a) and 13.77
Answers
13.34 (a) q =69.0 mW (b) qnet= 934.5 W/m2 (c) qnet, in = 1085 W/m2
13.58 (a) Ts =338K (b) 25.3 W/m2
13.62 T1 = 472C
13.71 (a)
13.77 Furnace Power required is 43.8 KW and T3 = 764 K